DATABASE TESTING INTERVIEW PART-2
Please go through the most frequently asked database testing interview topics.
Statements
They help us to create the table and insert the data.
There are 3 types of statements
- DDL – Data Definition Language – the various commands in DDL are:- Create, Drop, Truncate, Alter, Rename
- DML – Data Manipulation Language – the various commands in DML are:- Insert, Update, Delete
- TCL – Transaction Control Language – the various commands in TCL are:- Rollback, Commit, Savepoint
CREATE
It creates the table.
Before we study the Create command, let us first study some of the basic data types we use in SQL.
- CHAR
It stores the fixed-length character data.
It can store the alphanumeric data (i.e, numbers and characters).
- VARCHAR
It stores the variable-length character data It can store alphanumeric data.
In char, the maximum value we can store is 2000 characters
In varchar, the maximum value we can store is 4000 characters.
- NUMBER
It stores numeric data.
For ex – 1) sal number(4) ;
Here the maximum possible value is 9999.
sal number (6, 2) ;
Here, 2 – scale (total number of decimal places)
precision (total number of digits including decimal places) Maximum value is 9999.99
sal number (4, 3) ;
the maximum value is 9.999
sal number (2, 2)
the maximum value is .99
- DATE
– it stores date and time
– no need to specify any length for this type.
For ex, SQL > order_dt DATE ;
Date is always displayed in the default format:-
dd – month – yy
- BLOB
Stands for – Binary Large Object
It stores binary data (images, movies, music files) within the database. It stores up to 4GB.
- CLOB
Stands for – Character Large Object
It stores plain character data like varchar field up to 4GB.
Creating a table from another table
Now, we will see how to create a table from another table – i.e, it duplicates all the records and the characteristics of another table.
The SQL query for it is as follows

Thus we can see that we have created another table temp from table dept. We can verify it as shown below,
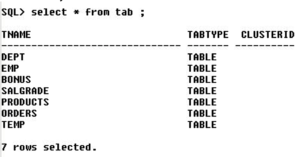
Thus, we can see that the table temp has been created.

Thus, we can see that the table temp has copied the structure of the table dept. Here, we must observe that temp copies all the columns, rows and NOT NULL constraints only from the table dept. It never copies PK, FK, Check constraints.
Thus, when in the interview somebody asks you “I have a table which has about 1million records. How do I duplicate it into another table without using Insert keyword and without inserting it individually all the records into the duplicated table?
The answer is – Use the above query of creating a table from another table and explain it.

Thus, from the above query – we can see that all the records of the table dept have been copied into the table temp.
TRUNCATE
It removes all the data permanently, but the structure of the table remains as it is.
Ex – SQL > TRUNCATE TABLE test ;
DROP
It removes both data and the structure of the table permanently from the database.
Ex – SQL > DROP TABLE test ;
Let us understand the difference between drop & truncate using the below-shown example,
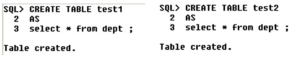
Let us create 2 tables Test1 and Test2 as shown above.

The above shows the description of table test1.

The above gives the description of table Test2.
Now, let us use the Truncate query on Test1 and Drop query on Test2 and see the difference.

The above 3 queries show that – 1 query has the table test1 truncated.
2nd query – it shows no rows selected – thus only the records from the table have been removed.
3rd query– it shows that the structure of the table is still present. Only the records will be removed. Thus, this explains the truncate query.
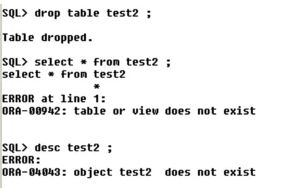
Thus from the above queries, we can explain how drop works. 1st query – it drops the table. Thus – the entire structure and records of the table are dropped. 2nd rd and 3 query – since there is no table – select & desc query for test2 will throw an error. Thus, this explains the drop query.
Hence, we have seen the difference between drop & truncate query.
10g Recycle Bin
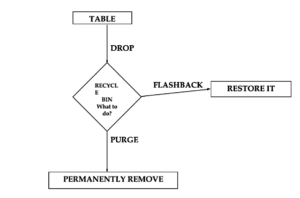
The functionality of Recycle Bin was introduced in Oracle 10G version only. Thus even though the table has been dropped, we can still restore it using flashback command or we can permanently remove it using the purge command.
This concept of Recycle bin was not there in the earlier versions of Oracle.
RENAME
It renames a table.
For example, let us see the query of how we do this renaming a table.
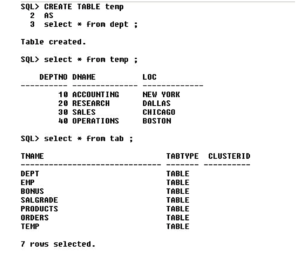
In the above 3queries – we have created a table temp which copies table dept – we see the records of the table temp – and also check if the table has really been created.
Now let us rename temp to temp23 as shown below,
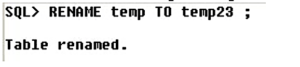
The above query is used to rename a table.
Now let us verify the contents of the table and check if it has really been modified, See next page,
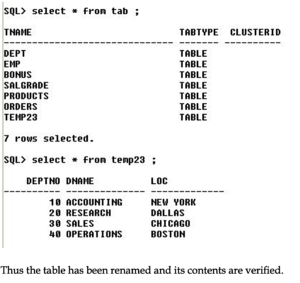
Thus the table has been renamed and its contents are verified.
ALTER
– this query alters/changes the structure of the table (i.e, – adding columns, removing columns, renaming columns etc ).
Now let us alter the table products (which we have created earlier).
1) Let us add a new column ‘model_no’ to the table.

Thus, a new column has been added. Let’s verify it with the query shown below,

2) Now let us drop the column model_no from products.
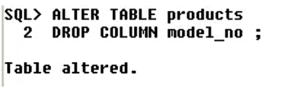
Thus, the column has been dropped.

Thus, we can see from the description of the table – the column model_no has been dropped.

Let us verify if it has been renamed,

NOTE: SELECT is neither DML nor DDL. It does not belong to any group because it does not alter anything, it just displays the data as required by the user.


Pingback: DATABASE TESTING INTERVIEW PART-1 - Software Testing Questions